UX | UI
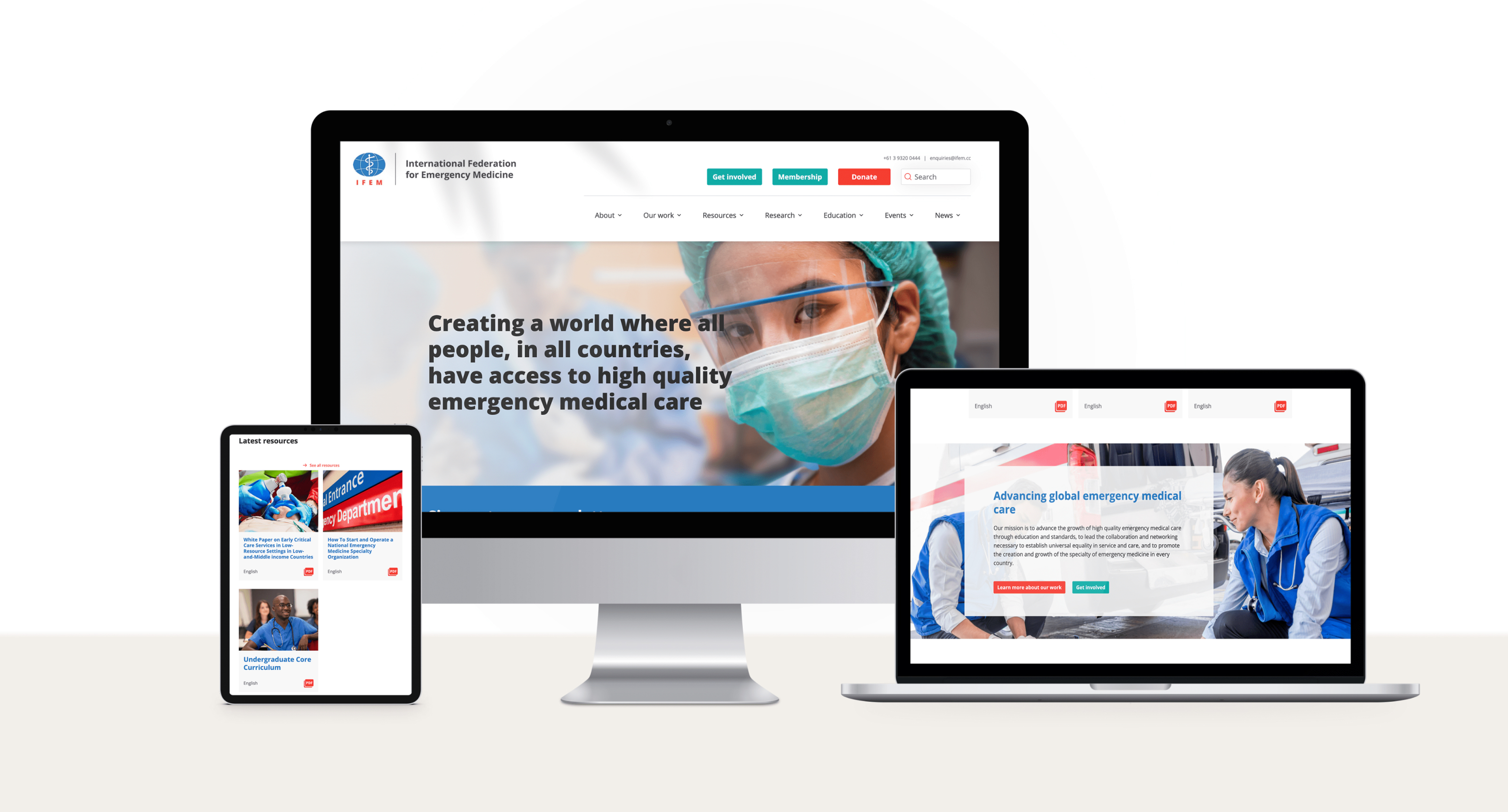
International Federation for Emergency Medicine
Emergency healthcare is a universal human right
International Federation for Emergency Medicine (IFEM) is a global organisation with the aim to ensure high quality emergency medical care for all people. IFEM works to achieve this through educating, advocating and supporting growth of the emergency medicine specialty in every country. IFEM wanted a website that would act as a living document of expertise, provide easy access to resources and facilitate networking between emergency medical workers from around the world. The new website would foster collaboration between health professionals on a global scale.
Goal
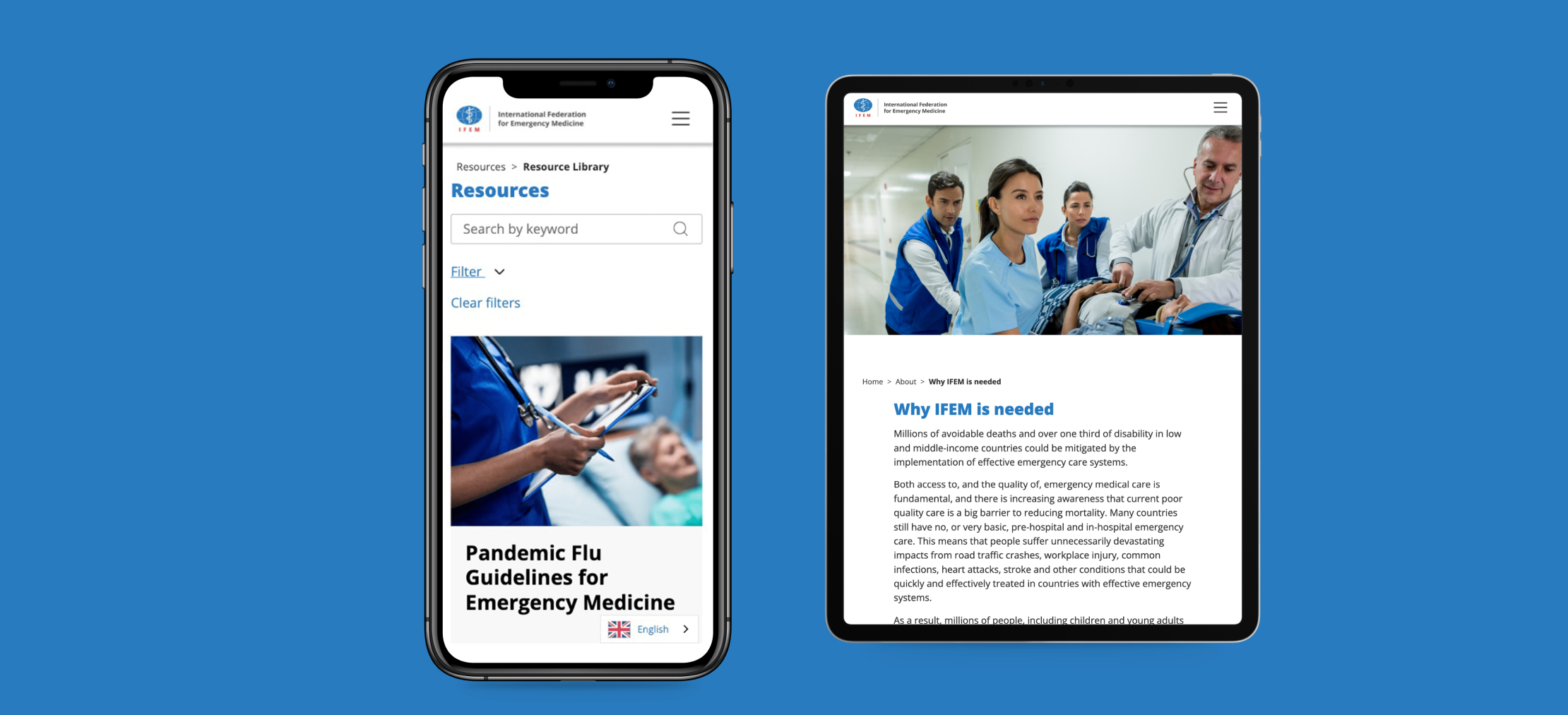
IFEM sought to build a new website that better serves its diverse global audience, including government policymakers, emergency care workers, students, and academic researchers. Given that emergency care professionals operate in a variety of resource, language, and cultural settings across different regions, the organization recognized the need for an accessible platform that supports those in low-resource environments.
The website needed to be intuitive, support multiple languages, and be optimized for users facing unreliable and expensive internet access, particularly in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. Additionally, the site had to host extensive information, including videos and PDFs, while ensuring seamless accessibility for all users.
Approach
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the audience’s needs, we engaged with over a hundred IFEM members, including emergency medical professionals from Africa, Asia, North America, Australasia, and Europe, through surveys. Our research also included an in-depth analysis of IFEM’s existing website analytics, allowing us to segment audiences based on their resource settings and access constraints.
We then conducted a series of interactive online workshops with over 20 IFEM members. These workshops helped identify key functionalities, critical content areas, and user preferences for website architecture. Participants shared their insights on how the website could better support networking, knowledge-sharing, and access to vital emergency care resources.
From our discovery phase, we identified three key priorities for the new website:
- Facilitating Connection & Collaboration – Enabling peer-to-peer networking and knowledge exchange.
- Supporting Diversity & Inclusion – Ensuring accessibility for various audiences, including those in low-resource settings.
- Enhancing Learning & Resource Sharing – Providing structured access to events, educational materials, and emergency care resources.
Solution
The website was built on NationBuilder, enabling it to host events, accept donations, and cater to different user journeys. A major focus was on accessibility for users with low bandwidth, which led us to optimize loading speeds, simplify key sections such as the resource hub, and minimize the use of large images and heavy scripts. By streamlining the design and functionality, we ensured that the most valuable content remained easily accessible, even in low-connectivity environments.
The new IFEM website has transformed how emergency care professionals across the world access information and connect with their peers. The improvements have led to:
- Increased engagement from healthcare workers in low-resource settings, who now have better access to vital emergency care materials.
- Faster loading speeds, ensuring usability for audiences with weak internet connections.
- A more intuitive and inclusive user experience that supports multiple languages and diverse accessibility needs.
- Enhanced networking opportunities, allowing professionals to collaborate, share best practices, and stay informed about global emergency care advancements.
Through a user-centered approach, we created a digital platform that aligns with IFEM’s mission, making emergency care knowledge more accessible and fostering a stronger global healthcare network.

Project Images


Before Images